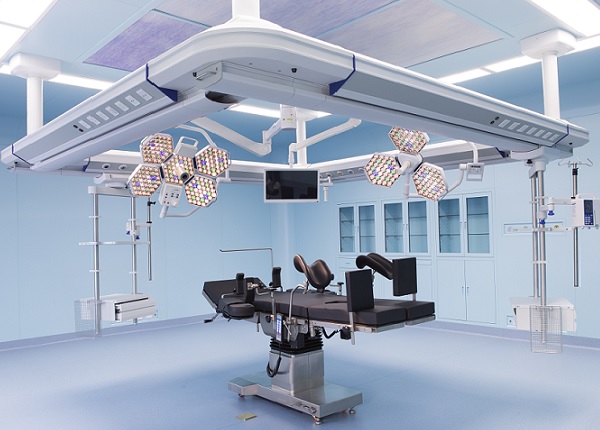
The efficient and safe operating room air purification system ensures the sterile environment of the operating room, and can meet the highly sterile environment required for organ transplantation, heart, blood vessel, artificial joint replacement and other operations.
The use of high-efficiency and low-toxic disinfectants, as well as rational use, are powerful measures to ensure the sterile environment of general operating rooms. According to constant discussion and repeated consideration, the revised “General Hospital Architectural Design Code”, the provisions on general operating rooms are finally determined as: “General operating rooms should use air-conditioning systems with terminal filters no lower than high-efficiency filters or fresh air. Ventilation system. Maintain positive pressure in the room, and the number of air changes shall not be less than 6 times/h”. For other parameters not involved, such as temperature and humidity, please refer to Class IV clean operating room.
Operating room classification
According to the degree of sterility or sterility of the operation, the operating room can be divided into the following five categories:
(1) Class I operating room: that is, the sterile purification operating room, which mainly accepts operations such as brain, heart, and organ transplantation.
(2) Class II operating room: the sterile operating room, which mainly accepts aseptic operations such as splenectomy, open reduction of closed fractures, intraocular surgery, and thyroidectomy.
(3) Class III operating room: that is, the operating room with bacteria, which accepts operations on the stomach, gallbladder, liver, appendix, kidney, lung and other parts.
(4) Class IV operating room: the infection operating room, which mainly accepts operations such as appendix perforation peritonitis surgery, tuberculous abscess, abscess incision and drainage, etc.
(5) Class V operating room: that is, the special infection operating room, which mainly accepts operations for infections such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus gas gangrene, and Bacillus tetanus.
According to different specialties, operating rooms can be divided into general surgery, orthopedics, obstetrics and gynecology, brain surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, urology, burns, ENT and other operating rooms. Since the operations of various specialties often require special equipment and instruments, the operating rooms for specialized operations should be relatively fixed.
A complete operating room includes the following parts:
①Sanitary passing room: including shoe changing room, dressing room, shower room, air shower room, etc.;
②Surgical room: including general operating room, sterile operating room, laminar flow purification operating room, etc.;
③ Surgical auxiliary room: including toilet, anesthesia room, resuscitation room, debridement room, plaster room, etc.;
④ Disinfection supply room: including disinfection room, supply room, equipment room, dressing room, etc.;
⑤ Laboratory diagnosis room: including X-ray, endoscopy, pathology, ultrasound and other inspection rooms;
⑥Teaching room: including operation observation table, closed-circuit television display classroom, etc.;
Regional division
The operating room must be strictly divided into restricted area (sterile operating room), semi-restricted area (contaminated operating room) and non-restricted area. There are two designs for the separation of the three areas: one is to set the restricted area and the semi-restricted area in two parts on different floors. This design can completely carry out hygiene isolation, but requires two sets of facilities, increases staff, and is inconvenient to manage; two In order to set up restricted areas and non-restricted areas in different sections of the same floor, the middle is transitioned from a semi-restricted area, and the equipment is shared, which is more convenient for design and management.
Restricted areas include sterile operating rooms, toilets, sterile rooms, drug storage rooms, etc. Semi-restricted areas include emergency operating rooms or contaminated operating rooms, equipment dressing preparation rooms, anesthesia preparation rooms, and disinfection rooms. In the non-restricted area, there are dressing rooms, plaster rooms, specimen rooms, sewage treatment rooms, anesthesia and recovery rooms, nurses’ offices, medical staff lounges, restaurants, and rest rooms for family members of surgical patients. The duty room and the nurse’s office should be located near the entrance.
Operating room location composition
The operating room should be located in a quiet, clean and convenient location for communication with relevant departments. Hospitals with low-level buildings as the main building should choose the flanks, and hospitals with high-rise buildings as the main body should choose the middle floor of the main building. The principle of location configuration of the operating room and other departments and departments is that it is close to the operating department, blood bank, imaging diagnosis department, laboratory diagnosis department, pathological diagnosis department, etc., which is convenient for work contact, and should be far away from boiler rooms, repair rooms, sewage treatment stations, etc. , to avoid pollution and reduce noise. The operating room should avoid direct sunlight as much as possible, it is easy to face north, or shaded by colored glass to facilitate artificial lighting. The orientation of the operating room should avoid air vents to reduce indoor dust density and air pollution. It is usually arranged in a centralized manner, forming a relatively independent medical area, including the operation part and the supply part.
Layout
The overall layout of the operating room department is very reasonable. Entering the operating room adopts a dual-channel solution, such as sterile surgical channels, including medical personnel channels, patient channels, and clean item supply channels; non-clean disposal channels:
Contaminated logistics of instruments and dressings after surgery. There is also a dedicated green channel for rescuing patients, so that critically ill patients can receive the most timely treatment. It can make the work of the operating department better achieve disinfection and isolation, clean and shunting, and avoid cross-infection to the greatest extent.
The operating room is divided into many operating rooms. According to the different levels of purification, there are two hundred-level operating rooms, two thousand-level operating rooms, and four ten-thousand-level operating rooms. Different levels of operating rooms have different uses: 100-level operating rooms Used for joint replacement, neurosurgery, cardiac surgery; Class 1000 operating room is used for a class of wound operations in orthopaedics, general surgery, and plastic surgery; Class 10,000 operating room is used for thoracic surgery, ENT, urology and general surgery In addition to the operation of a class of wounds; the operating room with positive and negative pressure switching can be used for special infection operations. Purifying air conditioning plays an irreplaceable role in preventing infection and ensuring the success of surgery, and is an indispensable supporting technology in the operating room. High-level operating rooms require high-quality clean air conditioners, and high-quality clean air conditioners can ensure a high level of operating rooms.
Air purification
The air pressure of the operating room varies according to the cleanliness requirements of different areas (such as operating room, sterile preparation room, brushing room, anesthesia room and surrounding clean areas, etc.). Different levels of laminar flow operating rooms have different air cleanliness standards. For example, the US Federal Standard 1000 is the number of dust particles ≥ 0.5 μm per cubic foot of air, ≤ 1000 particles or ≤ 35 particles per liter of air. The standard of 10000-level laminar flow operating room is the number of dust particles ≥0.5μm per cubic foot of air, ≤10000 particles or ≤350 particles per liter of air. And so on. The main purpose of operating room ventilation is to remove the exhaust gas in each workroom; to ensure the necessary amount of fresh air in each workroom; to remove dust and microorganisms; to maintain the necessary positive pressure in the room. There are two types of mechanical ventilation that can meet the ventilation requirements of the operating room. Combined use of mechanical air supply and mechanical exhaust: This ventilation method can control the number of air changes, air volume and indoor pressure, and the ventilation effect is better. Mechanical air supply and natural exhaust air are used together. The ventilation and ventilation times of this ventilation method are limited to a certain extent, and the ventilation effect is not as good as the former. The cleanliness level of the operating room is mainly distinguished by the number of dust particles in the air and the number of biological particles. Currently, the most commonly used is the NASA classification standard. The purification technology achieves the purpose of sterility by controlling the cleanliness of the air supply through positive pressure purification.
According to the different air supply methods, the purification technology can be divided into two types: turbulent flow system and laminar flow system. (1) Turbulence system (Multi-Directional Manner): The air supply port and high-efficiency filter of the turbulent flow system are located on the ceiling, and the air return port is located on both sides or the lower part of one side wall. The filter and air treatment are relatively simple, and the expansion is convenient. , The cost is low, but the number of air changes is small, generally 10 to 50 times/h, and it is easy to generate eddy currents, and the polluting particles may be suspended and circulated in the indoor eddy current area, forming a polluting airflow and reducing the indoor purification degree. Applicable only to 10,000-1,000,000 cleanrooms in NASA standards. (2) Laminal flow system: The laminar flow system uses air with uniform distribution and appropriate flow rate to bring particles and dust out of the operating room through the return air outlet, without generating eddy current, so there is no floating dust, and the degree of purification changes with the change. It can be improved by increasing the number of air times and is suitable for 100-level operating rooms in NASA standards. However, the damage rate of the filter seal is relatively large, and the cost is relatively high.
Operating room equipment
Operating room walls and ceilings are made of soundproof, solid, smooth, void-free, fireproof, moisture-proof, and easy-to-clean materials. Colors are light blue and light green. The corners are rounded to prevent dust accumulation. Film viewing lamps, medicine cabinets, consoles, etc. should be installed in the wall. The door should be wide and without threshold, which is convenient for flat cars to enter and exit. Avoid using spring doors that are easy to swing to prevent dust and bacteria from flying due to airflow. The windows should be double-layered, preferably aluminum alloy window frames, which are conducive to dustproof and thermal insulation. The window glass should be brown. The width of the corridor should be no less than 2.5m, which is convenient for the flat car to run and avoid collision between people passing by. Floors should be constructed of hard, smooth and easily scrubbed materials. The ground is slightly inclined to a corner, and a floor drain is set at the lower part to facilitate the discharge of sewage, and the drainage holes are covered to prevent polluted air from entering the room or being blocked by foreign objects.
The operating room power supply should have dual-phase power supply facilities to ensure safe operation. There should be enough electrical sockets in each operating room to facilitate the power supply of various instruments and equipment. The socket should be equipped with anti-spark device, and there should be conductive equipment on the ground of the operating room to prevent explosion caused by sparks. The electrical socket should be sealed with a cover to prevent water from entering, so as to avoid circuit failure affecting the operation. The main power line is centrally located in the wall, and the central suction and oxygen pipeline devices should be located in the wall. Lighting facilities General lighting should be installed on the wall or roof. Surgical lights should be installed with shadowless lights, and spare lifting lights. Water source and fire prevention facilities: taps should be installed in each workshop to facilitate flushing. Fire extinguishers should be installed in corridors and auxiliary rooms to ensure safety. Hot and cold water and high-pressure steam should be fully guaranteed. Ventilation, filtration and sterilization device: modern operating rooms should establish a perfect ventilation, filtration and sterilization device to purify the air. The ventilation methods include turbulent flow, laminar flow and vertical type, which can be selected as appropriate. Operating room entry and exit route layout: The layout design of the entry and exit routes must meet the requirements of functional processes and cleanliness partitions. Three entry and exit routes should be set up, one for staff entry and exit, the second for injured patients, and the third for circulating supply routes such as equipment dressings. , try to isolate and avoid cross-infection.
The temperature regulation of the operating room is very important, and there should be cooling and heating equipment. The air conditioner should be installed in the upper roof, the room temperature should be kept at 24-26℃, and the relative humidity should be about 50%. The general operating room is 35-45 square meters, and the special room is about 60 square meters, suitable for cardiopulmonary bypass surgery, organ transplantation, etc.; the small operating room area is 20-30 square meters.
Post time: Jul-08-2022